Insurance can seem complex, but breaking it down into its fundamental components—policies, premiums, and coverage options—makes it more accessible. Let’s explore these key aspects:
1. Insurance Policies
Definition: An insurance policy is a contract between the insurer (insurance company) and the insured (policyholder). It outlines the terms and conditions under which the insurer agrees to provide financial protection against specific risks.
Types of Policies:
Life Insurance: Provides a payout to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death.
Health Insurance: Covers medical expenses for illnesses, injuries, and other health-related issues.
Auto Insurance: Protects against financial loss due to accidents, theft, or damage to a vehicle.
Homeowners/Renters Insurance: Covers damage to property and belongings, and liability for accidents that occur on the premises.
Disability Insurance: Provides income replacement if the policyholder becomes unable to work due to disability.
2. Premiums
Definition: A premium is the amount you pay to the insurance company in exchange for coverage. Premiums can be paid monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually.
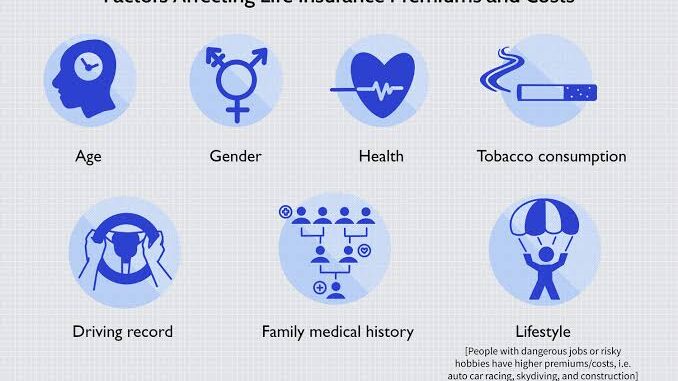
Factors Affecting Premiums:
Age: Younger people often pay lower premiums, especially for life and health insurance.
Health: Healthier individuals typically get better rates for life and health insurance.
Coverage Amount: Higher coverage amounts generally result in higher premiums.
Risk Factors: In auto insurance, factors like driving history, vehicle type, and location can impact premiums.
Deductibles: Higher deductibles (the amount paid out of pocket before insurance kicks in) usually lead to lower premiums.
3. Coverage Options
Definition: Coverage refers to the specific protection provided by an insurance policy. It outlines what is and isn’t covered, including the limits and exclusions.
Key Considerations:
Limits: The maximum amount the insurer will pay for a covered loss. For example, an auto insurance policy might have a limit of $100,000 for liability coverage.
Exclusions: Situations or conditions not covered by the policy. For example, a health insurance policy may not cover cosmetic procedures.
Riders/Endorsements: Additional provisions that can be added to a policy to provide extra coverage or modify the terms. For instance, a jewelry rider can be added to a homeowners policy to cover valuable items.
Making Informed Choices
When selecting an insurance policy, it’s essential to:
Assess Your Needs: Consider what you need protection against and choose a policy that matches those needs.
Compare Policies: Look at different insurers and policies to find the best coverage at the most affordable premium.
Understand the Terms: Read the policy documents carefully to understand what’s covered, the limits, exclusions, and your obligations.
Understanding these components helps demystify insurance, enabling you to make informed decisions that protect yo
u and your loved ones financially.